|
A genetic algorithm with feasibility-agnostic encoding and three-phase decoding for scheduling problems in semiconductor manufacturing
In-Beom Park, Jaeseok Huh*
@article{park2026genetic,
title={A genetic algorithm with feasibility-agnostic encoding and three-phase decoding for scheduling semiconductor manufacturing facilities under queue time limits},
author={Park, In-Beom and Huh, Jaeseok},
journal={Expert Systems with Applications},
volume={301},
pages={130310},
year={2026},
publisher={Elsevier}
}
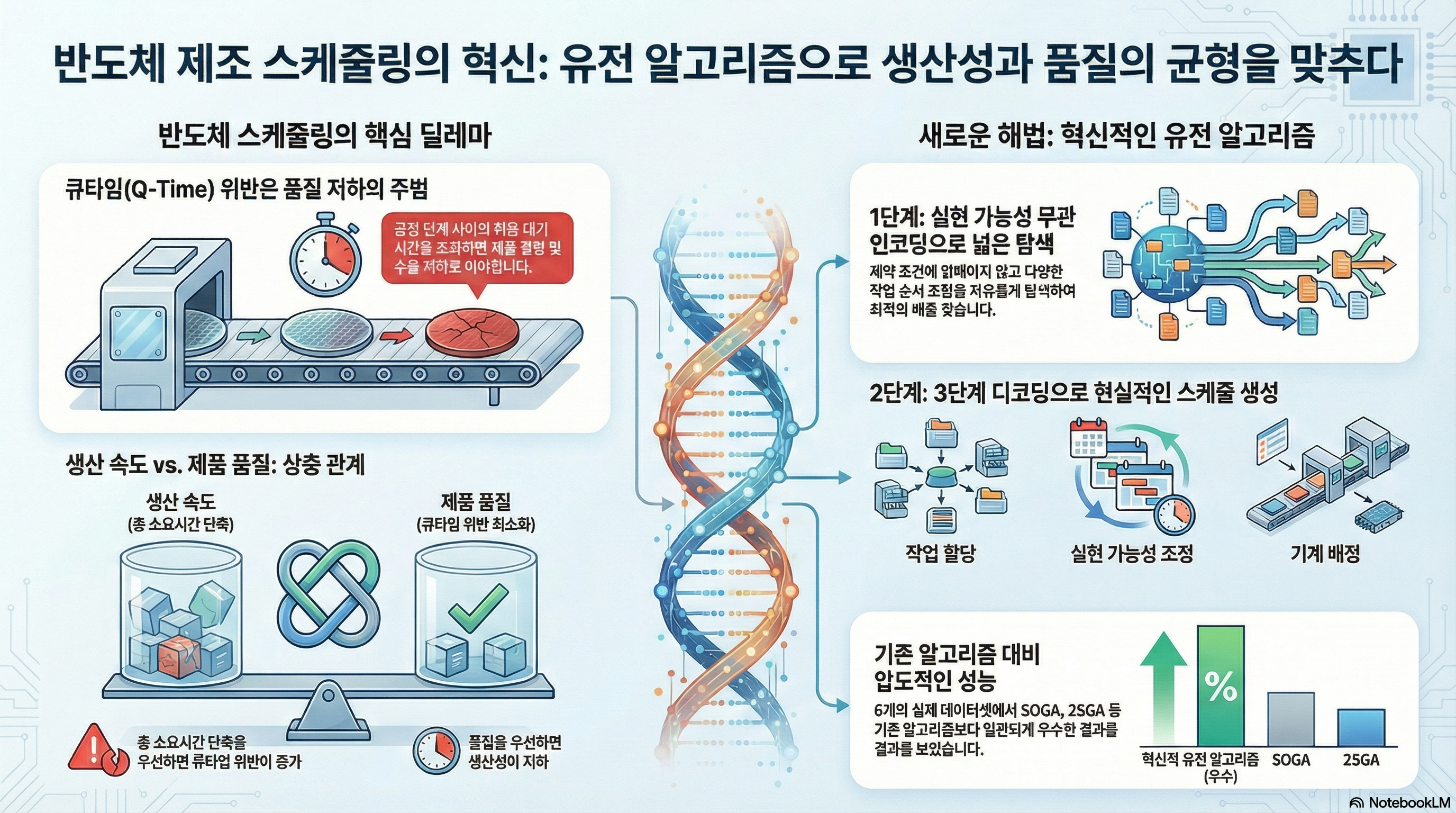
Queue time (Q-time) limits, which refer to the allowable time intervals between consecutive processing steps, play an essential role in the semiconductor industry. This importance stems from the fact that violations of Q-time limits are highly likely to degrade product quality and yield, ultimately resulting in resource waste, reprocessing, and increased environmental impact. To address these challenges, we propose a novel genetic algorithm for solving scheduling problems in semiconductor manufacturing facilities with sequence-dependent setups, aiming to minimize a weighted sum of the makespan and the total time exceeding the Q-time limits. Specifically, we introduce a feasibility-agnostic encoding scheme and a three-phase decoding procedure that consists of job assignment, feasibility adjustment, and machine allocation. Furthermore, customized crossover and mutation operators are incorporated to enhance the exploration of the solution space. Comprehensive experiments on six datasets demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method compared to other metaheuristics. Based on the improvement of baseline metaheuristics when initialized with the solutions generated by the proposed encoding and decoding procedures, we verify the viability of the proposed method.
Expert Systems with Applications, 2026
|
|
Metaheuristic-based weight optimization for robust deep reinforcement learning in continuous control
Gwang-Jong Ko, Jaeseok Huh*
@article{ko2025metaheuristic,
title={Metaheuristic-based weight optimization for robust deep reinforcement learning in continuous control},
author={Ko, Gwang-Jong and Huh, Jaeseok},
journal={Swarm and Evolutionary Computation},
volume={95},
pages={101920},
year={2025},
publisher={Elsevier}
}
In recent studies, the policy-based deep reinforcement learning (DRL) algorithms have exhibited superior performance in addressing continuous control problems, such as machine arms control and robot gait learning. However, these algorithms frequently face challenges inherent in gradient descent-based weight optimization methods, including susceptibility to local optima, slow learning speeds due to saddle points, approximation errors, and suboptimal hyperparameters. This instability leads to significant performance discrepancies among agent instances trained under identical settings, which complicates the practical application of reinforcement learning. To address this, we propose a metaheuristic-based weight optimization framework designed to mitigate learning instability in DRL for continuous control tasks. The proposed framework introduces a two-phase optimization process, where an additional search phase using swarm intelligence algorithms is conducted at the end of the learning phase utilizing DRL. In numerical experiments, the proposed framework demonstrated superior and more stable performance compared to conventional DRL algorithms in robot locomotion tasks.
Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2025
|
|
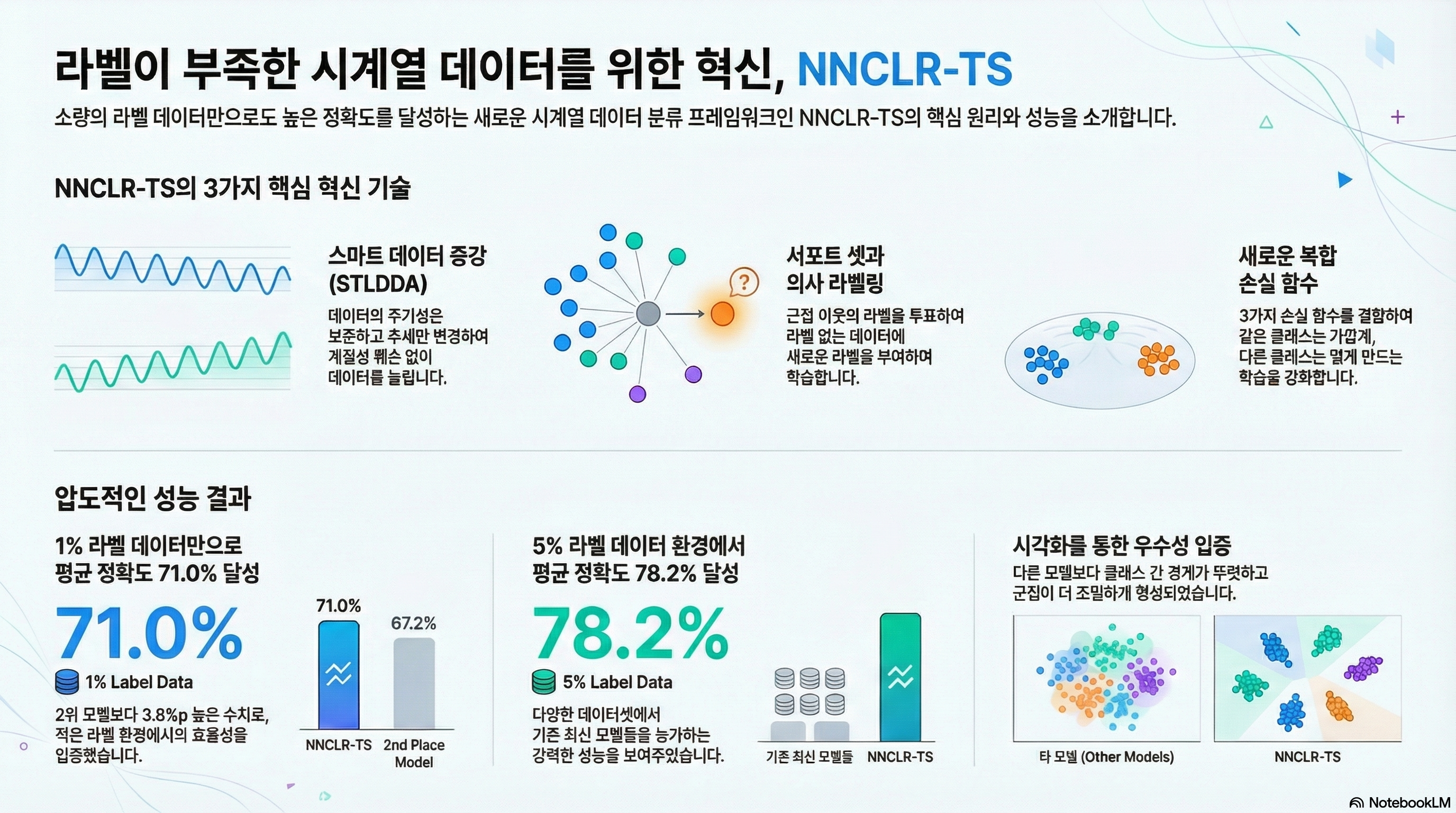
Semi-supervised contrastive learning with decomposition-based data augmentation for time series classification
Dokyun Kim, Sukhyun Cho, Heewoong Chae, Jonghun Park, Jaeseok Huh*
@article{kim2025ida,
title={Semi-supervised contrastive learning with decomposition-based data augmentation for time series classification},
author={Kim, Dokyun and Cho, Sukhyun and Chae, Heewoong and Park, Jonghun and Huh, Jaeseok},
journal={Intelligent Data Analysis},
volume={29},
number={1},
pages={94--115},
year={2025},
publisher={SAGE Publications}
}
While time series data are prevalent across diverse sectors, data labeling process still remains resource-intensive. This results in a scarcity of labeled data for deep learning, emphasizing the importance of semi-supervised learning techniques. Applying semi-supervised learning to time series data presents unique challenges due to its inherent temporal complexities. Efficient contrastive learning for time series requires specialized methods, particularly in the development of tailored data augmentation techniques. In this paper, we propose a single-step, semi-supervised contrastive learning framework named nearest neighbor contrastive learning for time series (NNCLR-TS). Specifically, the proposed framework incorporates a support set to store representations including their label information, enabling a pseudo-labeling of the unlabeled data based on nearby samples in the latent space. Moreover, our framework presents a novel data augmentation method, which selectively augments only the trend component of the data, effectively preserving their inherent periodic properties and facilitating effective training. For training, we introduce a novel contrastive loss that utilizes the nearest neighbors of augmented data for positive and negative representations. By employing our framework, we unlock the ability to attain high-quality embeddings and achieve remarkable performance in downstream classification tasks, tailored explicitly for time series. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches across various benchmarks, validating the effectiveness of our proposed method.
Intelligent Data Analysis, 2025
|
|
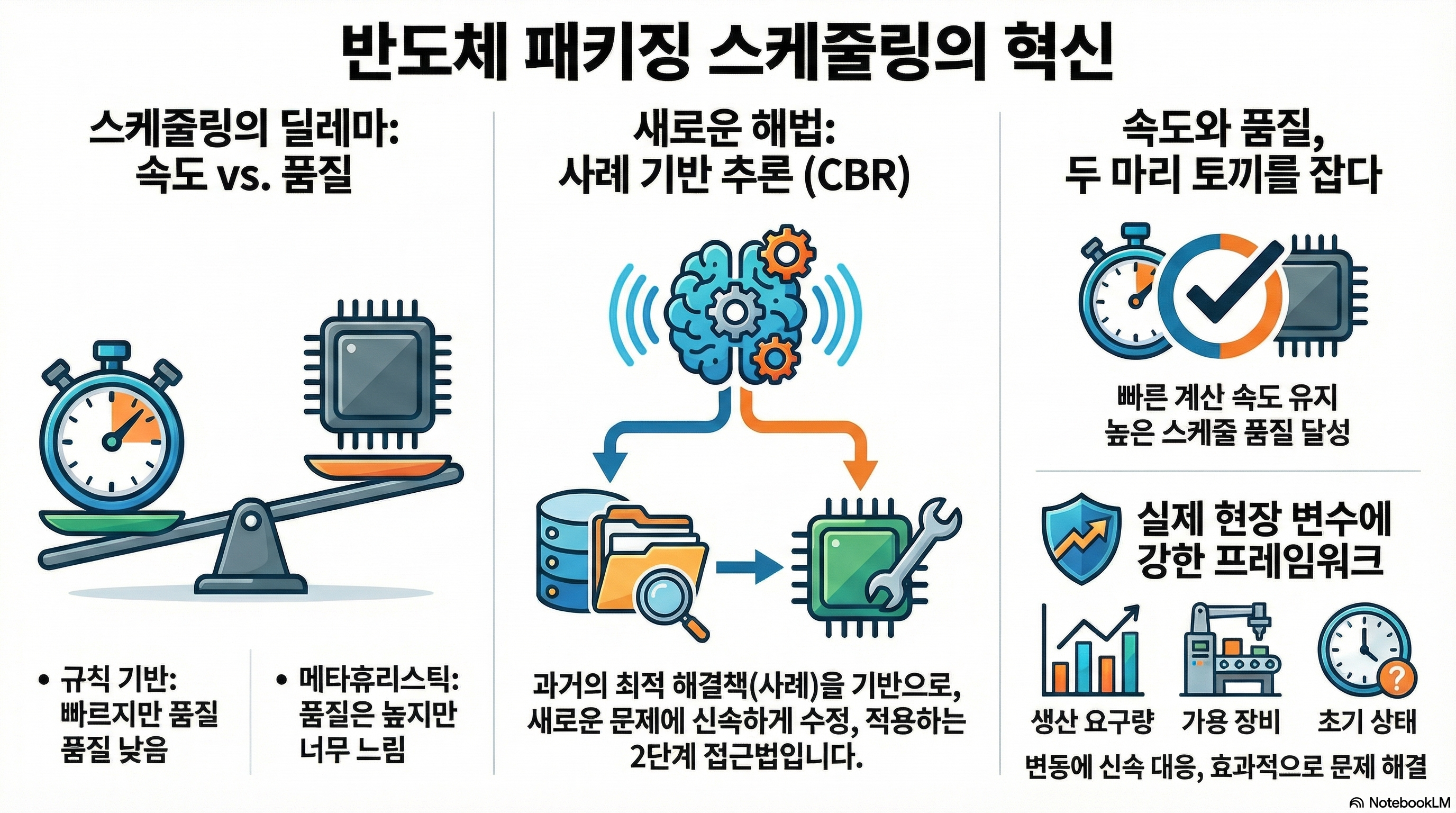
A generation and repair approach to scheduling semiconductor packaging facilities using case-based reasoning
In-Beom Park, Jaeseok Huh*, Jonghun Park
@article{park2023generation,
title={A generation and repair approach to scheduling semiconductor packaging facilities using case-based reasoning},
author={Park, In-Beom and Huh, Jaeseok and Park, Jonghun},
journal={IEEE Access},
volume={11},
pages={50631--50641},
year={2023},
publisher={IEEE}
}
As the demand for multi-chip products with high capacity and small size increases, semiconductor packaging facilities have been faced with complicated constraints such as re-entrant flows, sequence dependent setups, and alternative routes, which leads to difficulties in scheduling semiconductor manufacturing operations. Furthermore, due to the frequent variations in the relative importance between objectives as well as the variabilities in initial setup status, available machines, and production requirements, practitioners are obliged to obtain a schedule within a short amount of computation time. In this paper, we propose a novel two-phase framework that aims to quickly produce a schedule of semiconductor packaging facilities by using case-based reasoning for minimizing the weighted sum of machine loss time and waiting time of jobs. Specifically, in the case generation phase, a case database is constructed by solving case scheduling problems using an existing solver. The case reasoning phase is responsible for repairing operation type sequences in the cases to produce a schedule for an unseen scheduling problem whose production requirements, available machines, initial setup status, and weight between performance measures are different from those of cases. The extensive experimental results demonstrated that the proposed approach requires a short computation time similar to the rule-based methods while maintaining the quality of the schedules comparable to that of the existing metaheuristics.
IEEE Access, 2023
|

|
A reinforcement learning approach to robust scheduling of semiconductor manufacturing facilities
In-Beom Park, Jaeseok Huh*, Joongkyun Kim, Jonghun Park
@article{park2020tase,
title={A reinforcement learning approach to robust scheduling of semiconductor manufacturing facilities},
author={Park, In-Beom and Huh, Jaeseok and Kim, Joongkyun and Park, Jonghun},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering},
volume={17},
number={3},
pages={1420--1431},
year={2020},
publisher={IEEE}
}
As semiconductor manufacturers, recently, have focused on producing multichip products (MCPs), scheduling semiconductor manufacturing operations become complicated due to the constraints related to reentrant production flows, sequence-dependent
setups, and alternative machines. At the same time, the scheduling problems need to be solved frequently to effectively
manage the variabilities in production requirements, available machines, and initial setup status. To minimize the makespan
for an MCP scheduling problem, we propose a setup change scheduling method using reinforcement learning (RL) in which each
agent determines setup decisions in a decentralized manner and learns a centralized policy by sharing a neural network among
the agents to deal with the changes in the number of machines. Furthermore, novel definitions of state, action, and reward
are proposed to address the variabilities in production requirements and initial setup status. Numerical experiments demonstrate
that the proposed approach outperforms the rule-based, metaheuristic, and other RL methods in terms of the makespan while
incurring shorter computation time than the metaheuristics considered.
IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2020
|
|
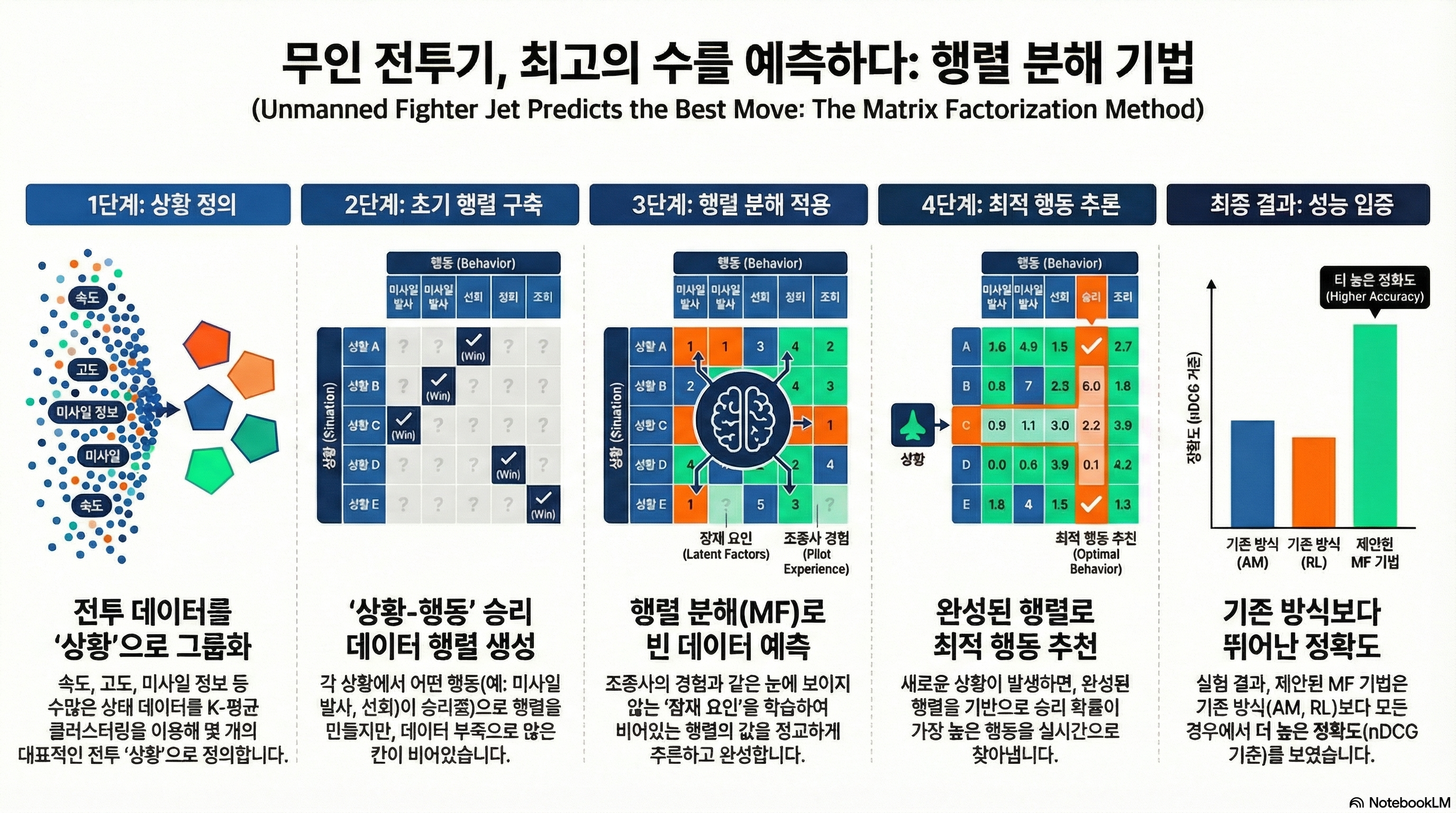
A Behavior optimization method for unmanned combat aerial vehicles using matrix factorization
Jaeseok Huh, Jonghun Park, Dongmin Shin, Yerim Choi*
@article{huh2020ieeeaccess,
title={A Behavior optimization method for unmanned combat aerial vehicles using matrix factorization},
author={Huh, Jaeseok and Park, Jonghun and Shin, Dongmin and Choi, Yerim},
journal={IEEE Access},
volume={8},
pages={100298--100307},
year={2020},
publisher={IEEE}
}
One of the fundamental technologies for unmanned combat aerial vehicles and combat simulators is behavior optimization, which identifies a behavior that maximizes the probability of winning a battle. With the advent of military science, combat logs became available, allowing machine learning algorithms to be applied for behavior optimization. However, implicit attributes such as operator experience, not explicitly recorded in log data, limit the performance of existing methods. Additionally, the low frequency of specific behaviors creates datasets with imbalanced and missing values. To address these issues, we apply a matrix factorization (MF) method, a latent factor model well-suited for sophisticated imputation of missing values, to the behavior optimization problem. A situation–behavior matrix, whose elements are ratings of behavior optimality in given situations, is constructed. Experiments conducted with combat logs demonstrate that the proposed MF-based method achieves satisfactory performance compared to existing approaches.
IEEE Access, 2020
|
|
A hierarchical SVM based behavior inference of human operators using a hybrid sequence kernel
Jaeseok Huh, Jonghun Park, Dongmin Shin, Yerim Choi*
@article{huh2019hierarchical,
title={A hierarchical SVM based behavior inference of human operators using a hybrid sequence kernel},
author={Huh, Jaeseok and Park, Jonghun and Shin, Dongmin and Choi, Yerim},
journal={Sustainability},
volume={11},
number={18},
pages={4836},
year={2019},
publisher={MDPI}
}
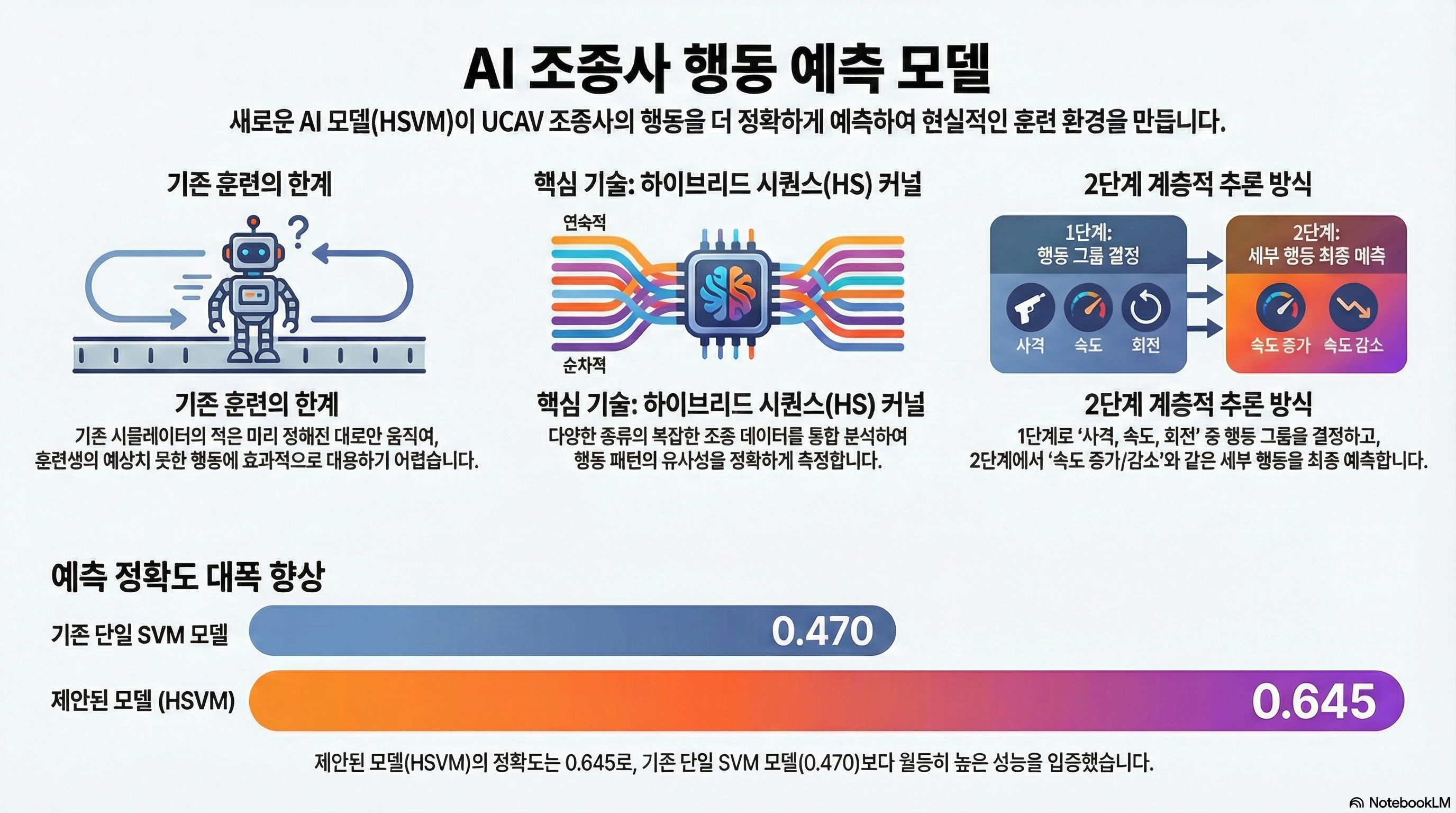
To train skilled unmanned combat aerial vehicle (UCAV) operators, it is important to establish a real-time training environment where an enemy appropriately responds to the action performed by a trainee. This can be addressed by constructing the inference method for the behavior of a UCAV operator from given simulation log data. Through this method, the virtual enemy is capable of performing actions that are highly likely to be made by an actual operator. To achieve this, we propose a hybrid sequence (HS) kernel-based hierarchical support vector machine (HSVM) for the behavior inference of a UCAV operator. Specifically, the HS kernel is designed to resolve the heterogeneity in simulation log data, and HSVM performs the behavior inference in a sequential manner considering the hierarchical structure of the behaviors of a UCAV operator. The effectiveness of the proposed method is demonstrated with the log data collected from the air-to-air combat simulator.
Sustainability, 2019
|
|
A case-based reasoning approach to fast optimization of travel routes for large-scale AS/RSs
Jaeseok Huh, Moon-jung Chae, Jonghun Park, Kwanho Kim*
@article{huh2019jim,
title={A case-based reasoning approach to fast optimization of travel routes for large-scale AS/RSs},
author={Huh, Jaeseok and Chae, Moon-jung and Park, Jonghun and Kim, Kwanho},
journal={Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing},
volume={30},
number={4},
pages={1765--1778},
year={2019},
publisher={Springer}
}
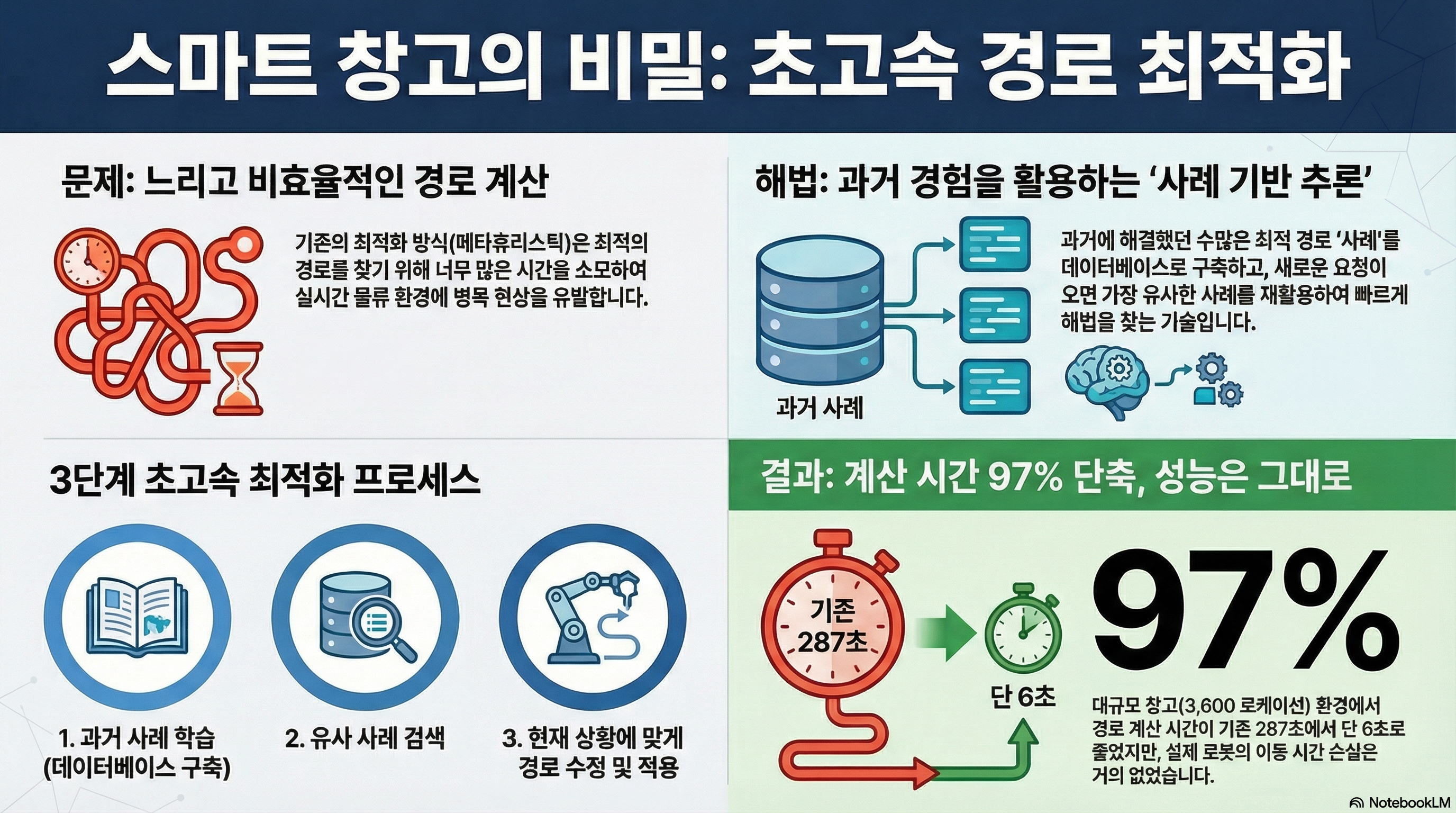
Due to the increasing volume of stocks in modern production and logistics environments, the scale of automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RSs) is becoming significantly large. To optimize travel routes for such large-scale AS/RSs, excessive computation complexity is unavoidable when applying existing metaheuristics due to their exhaustive nature. In this paper, we propose a case-based reasoning method for quickly optimizing travel routes. In the casebase construction phase, the method stores a large number of cases, each consisting of the optimized travel route for a particular setting. In the reasoning phase, the travel routes in the cases are then repaired to determine the optimal travel route for the current setting. Experimental results show that the proposed method successfully yields optimized travel routes in a short time compared to conventional methods, even for real-world scale problems.
Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2019
|
|
Learning to dispatch operations with intentional delay for re-entrant multiple-chip product assembly lines
Jaeseok Huh, Inbeom Park, Seongmin Lim, Paeng Bohyung, Jonghun Park, Kwanho Kim*
@article{huh2018learning,
title={Learning to dispatch operations with intentional delay for re-entrant multiple-chip product assembly lines},
author={Huh, Jaeseok and Park, Inbeom and Lim, Seongmin and Paeng, Bohyung and Park, Jonghun and Kim, Kwanho},
journal={Sustainability},
volume={10},
number={11},
pages={4123},
year={2018},
publisher={MDPI}
}
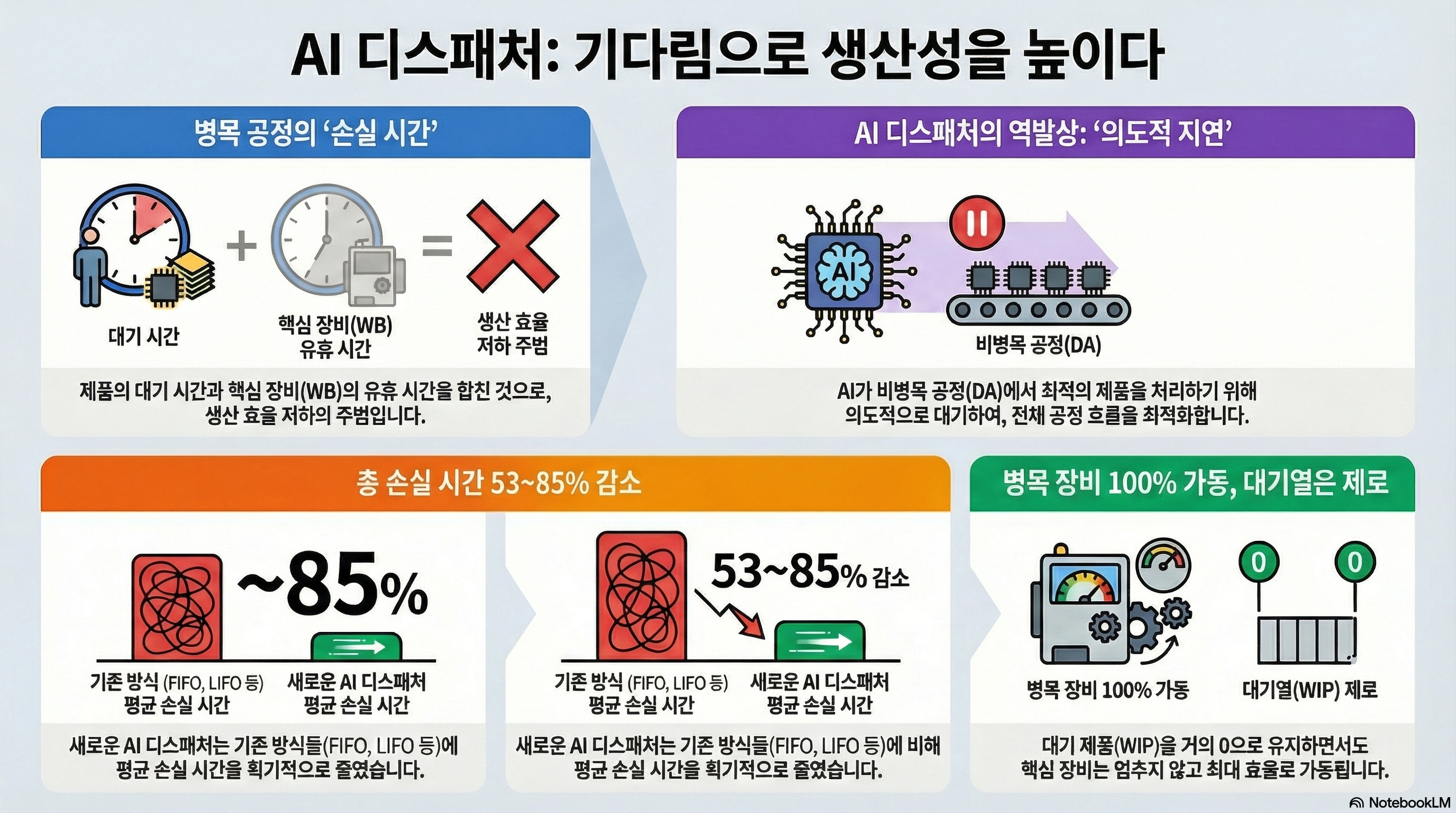
As the demand for small devices with embedded flash memory increases, semiconductor manufacturers have been recently focusing on producing high-capacity multiple-chip products (MCPs). Due to the frequently re-entrant lots between the die attach (DA) and wire bonding (WB) assembly stages in MCP production, increased flow time and decreased resource utilization are unavoidable. In this paper, we propose a dispatcher based on artificial neural networks, which minimizes the flow time while maintaining high utilization of resources at the same time through exploiting the possible intentional delays on DA stage. Specifically, the proposed dispatcher learns the assignment preferences between available lots and DA resources based on assembly line data generated by using a simulator, then the proposed dispatcher performs lot dispatching decisions by considering the intentional delays. The numerical experiments were performed under various configurations of the MCP assembly lines, and the results show that the proposed dispatcher outperformed the existing methods.
Sustainability, 2018
|
|
LiveGantt: Interactively Visualizing a Large Manufacturing Schedule
Jaemin Jo, Jaeseok Huh, Jonghun Park, Bohyoung Kim, Jinwook Seo*
@article{jo2014livegantt,
title={LiveGantt: Interactively visualizing a large manufacturing schedule},
author={Jo, Jaemin and Huh, Jaeseok and Park, Jonghun and Kim, Bohyoung and Seo, Jinwook},
journal={IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics},
volume={20},
number={12},
pages={2329--2338},
year={2014},
publisher={IEEE}
}
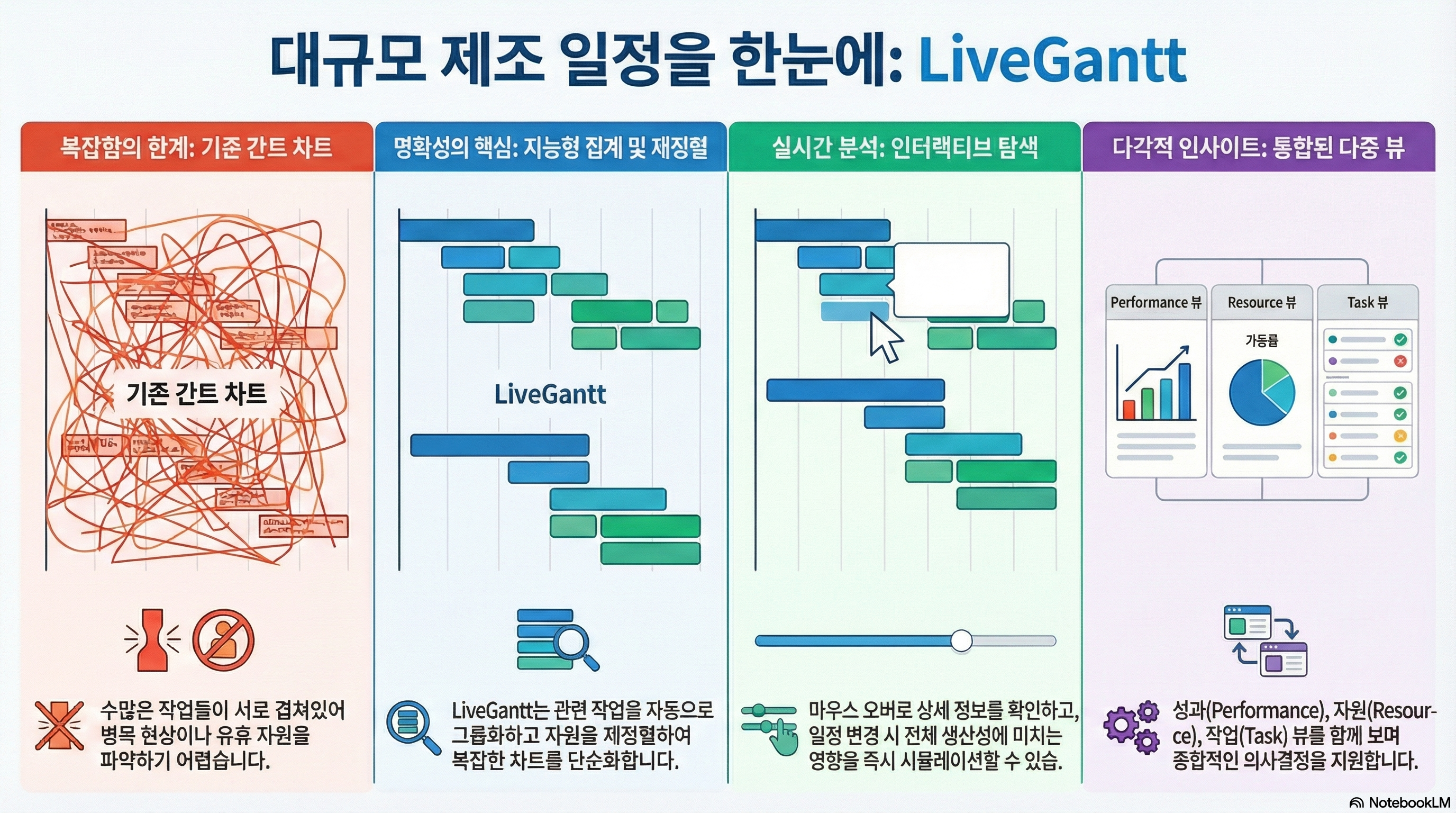
In this paper, we introduce LiveGantt as a novel interactive schedule visualization tool that helps users explore highly-concurrent large schedules from various perspectives. Although a Gantt chart is the most common approach to illustrate schedules, currently available Gantt chart visualization tools suffer from limited scalability and lack of interactions. LiveGantt is built with newly designed algorithms and interactions to improve conventional charts with better scalability, explorability, and reschedulability. It employs resource reordering and task aggregation to display the schedules in a scalable way. LiveGantt provides four coordinated views and filtering techniques to help users explore and interact with the schedules in more flexible ways. In addition, LiveGantt is equipped with an efficient rescheduler to allow users to instantaneously modify their schedules based on their scheduling experience in the fields. To assess the usefulness of the application of LiveGantt, we conducted a case study on manufacturing schedule data with four industrial engineering researchers. Participants not only grasped an overview of a schedule but also explored the schedule from multiple perspectives to make enhancements.
IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics, 2014
|
|
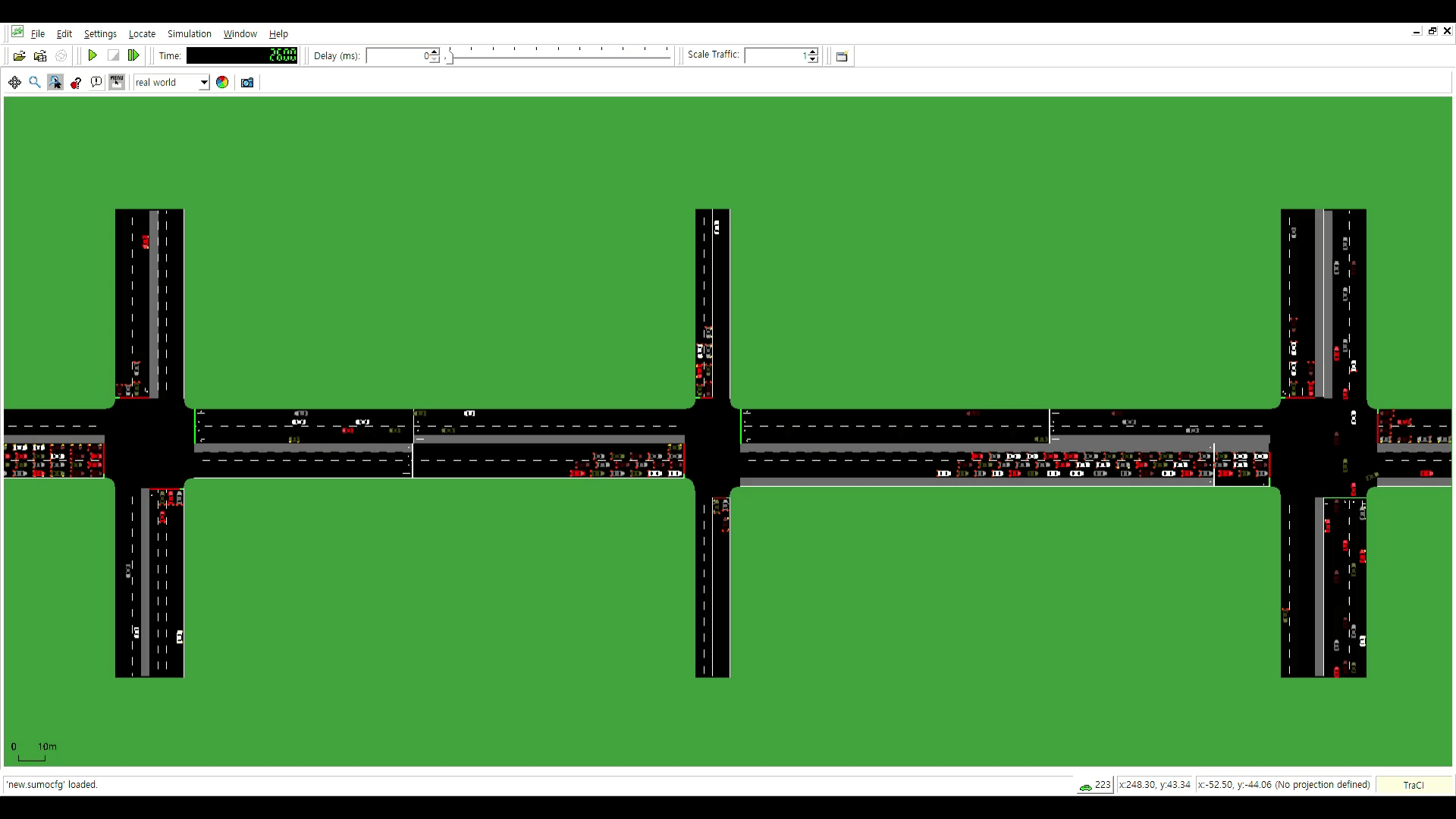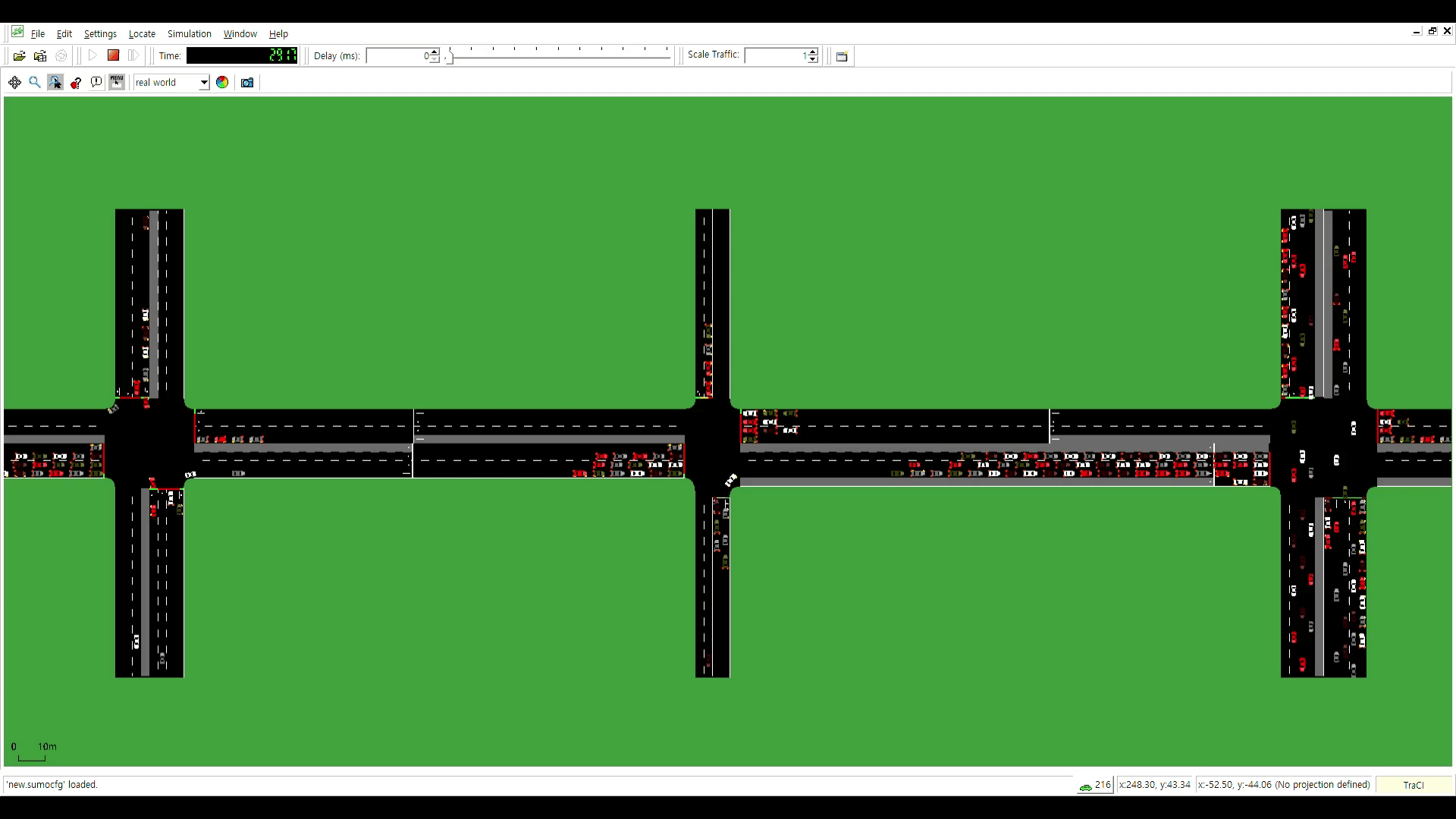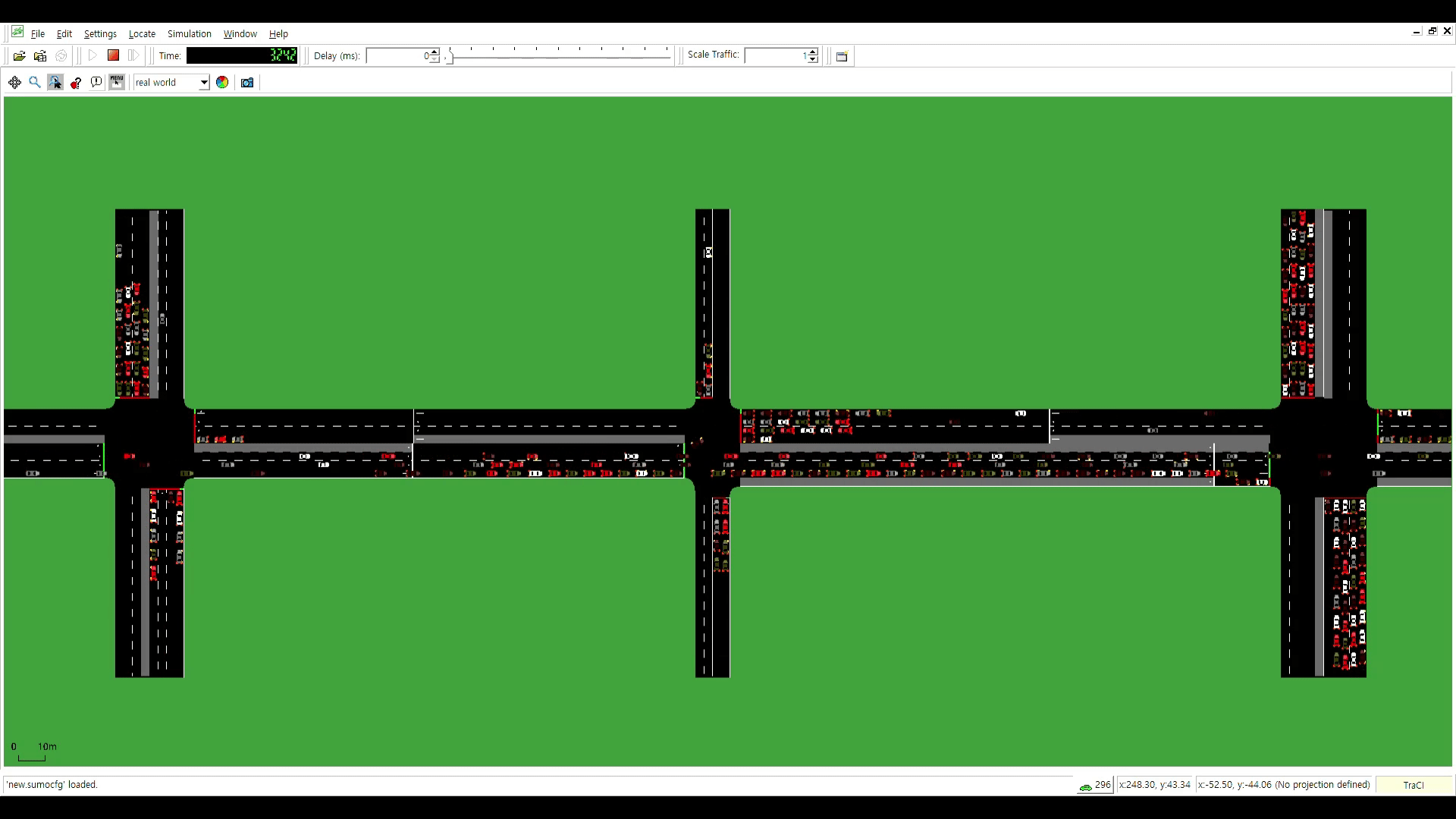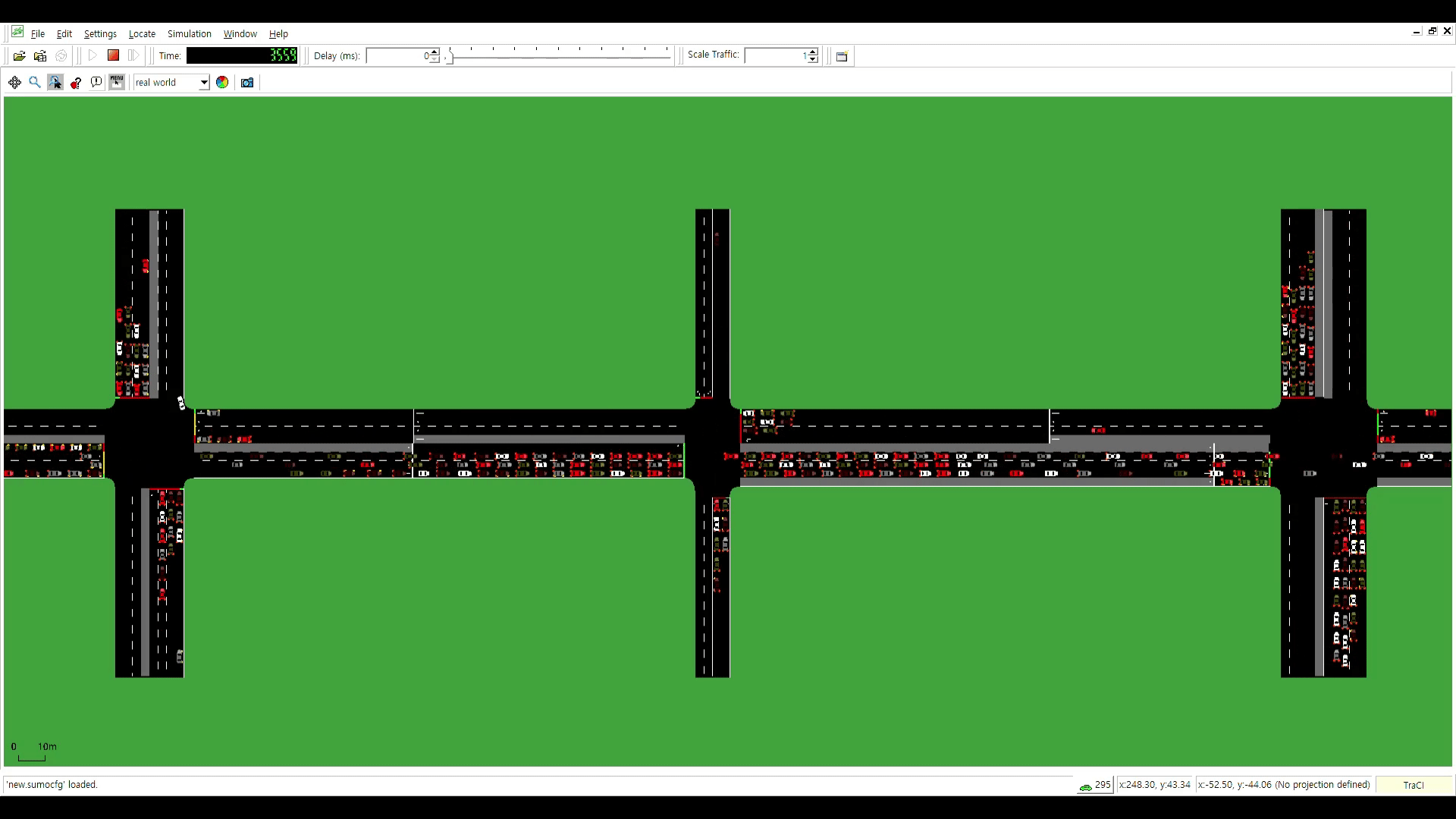
공통 신호주기 제약을 고려한 Particle Swarm Optimization 기반 다중 교차로 교통 신호 최적화
박진환, 허재석*
@article{park2024pso,
title={공통 신호주기 제약을 고려한 Particle Swarm Optimization 기반 다중 교차로 교통 신호 최적화},
author={박진환 and 허재석},
journal={대한산업공학회지},
volume={50},
number={5},
pages={313--324},
year={2024}
}
Traffic congestion frequently occurs at multiple intersections with high vehicular traffic, particularly during rush hour. Inconsistent signal cycle lengths across intersections can hinder traffic flow, even when an upstream intersection grants a green light. To address this, the signal cycle lengths of multiple intersections should be identical. Furthermore, practical constraints must be considered- (1) all signal times must be integers, (2) phase sequences should remain fixed to prevent accidents and driver confusion, and (3) pedestrian safety must be ensured through sufficient crossing time. This paper proposes a novel particle swarm optimization-based method for optimizing traffic signals at multiple intersections, addressing the need for consistent signal cycle lengths and the practical constraints. The proposed method was evaluated using the traffic simulator SUMO (Simulation of Urban Mobility). Compared to existing signals, the proposed method reduced the average waiting time of vehicles passing through multiple intersections by 10% during morning rush hour, 20% during normal hour, and 31% during evening rush hour.
대한산업공학회지, 2024
|
|
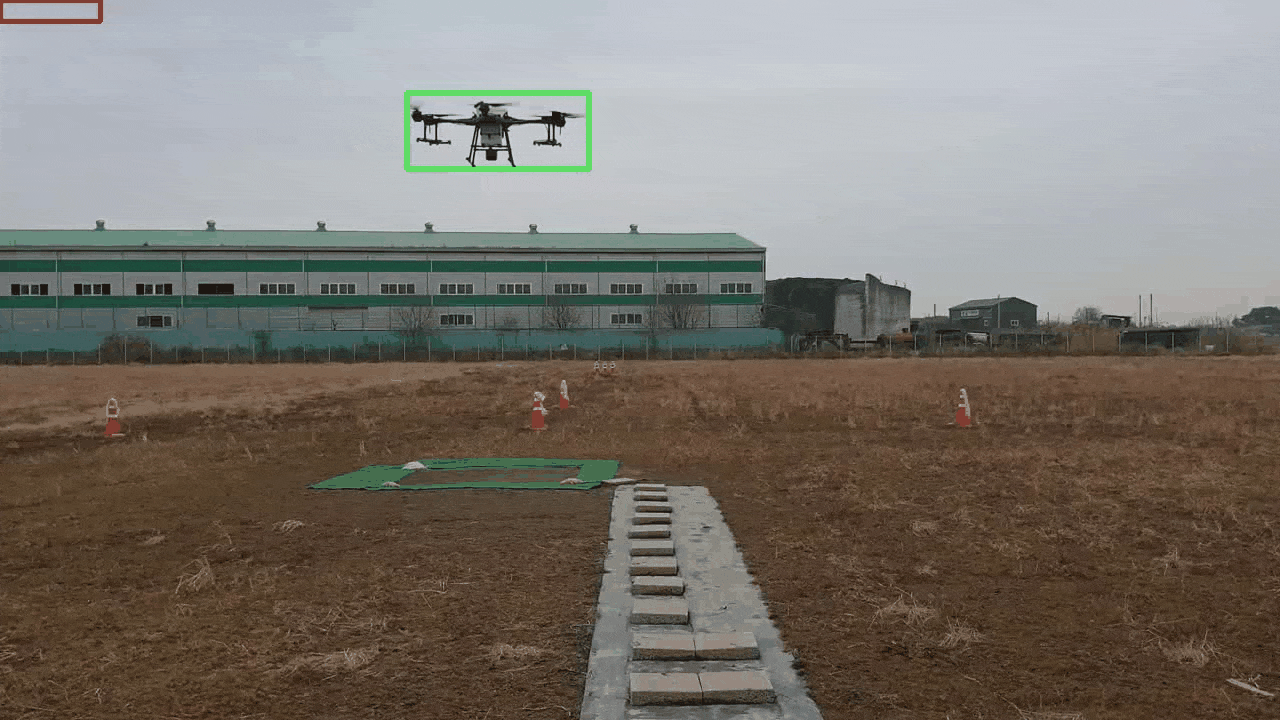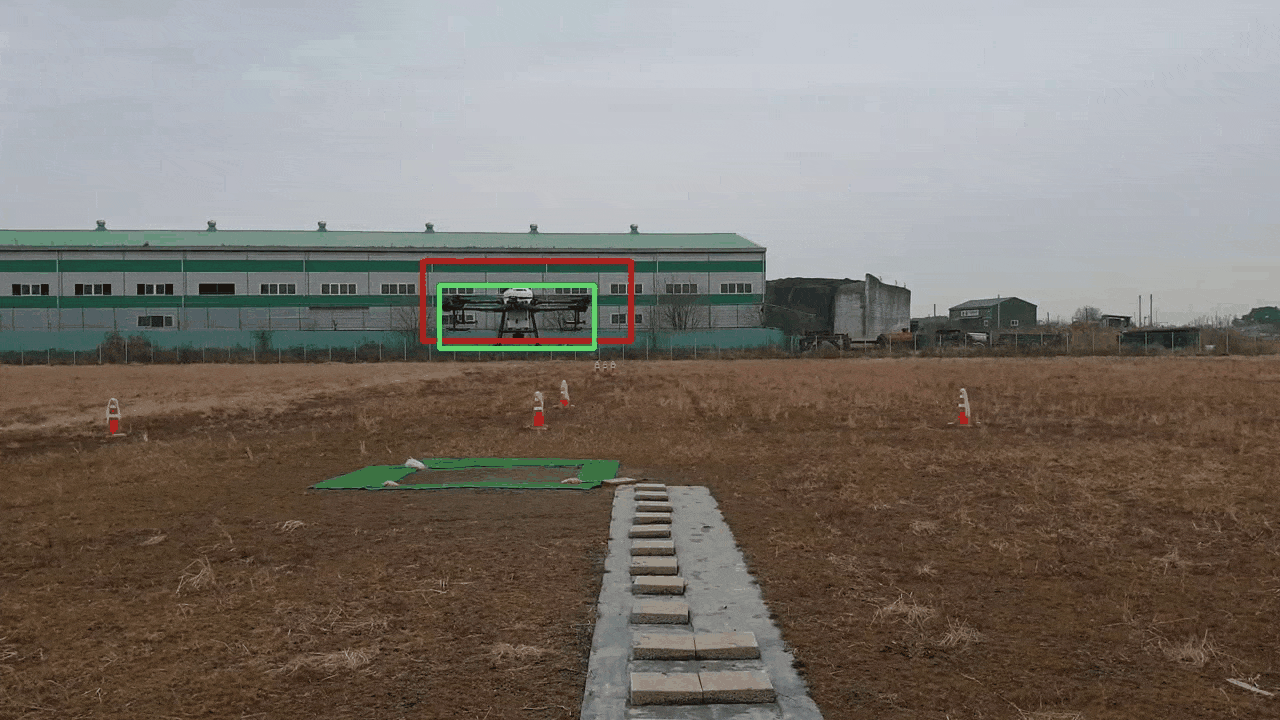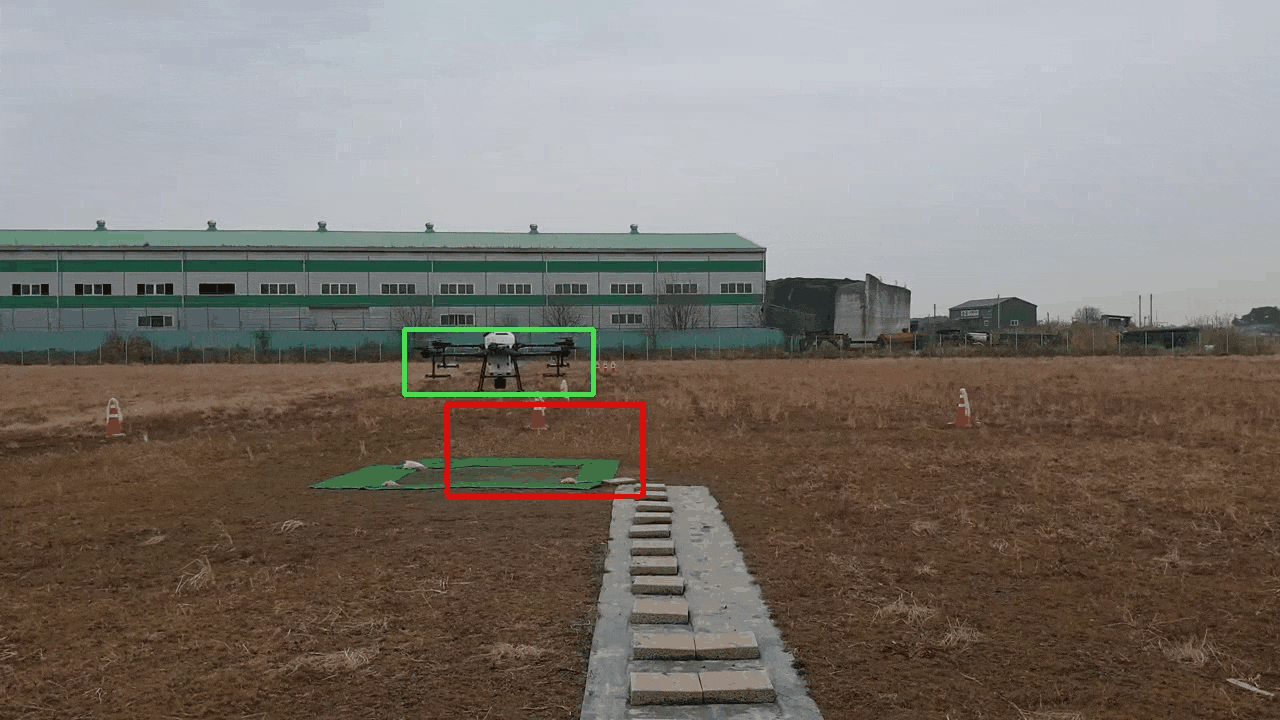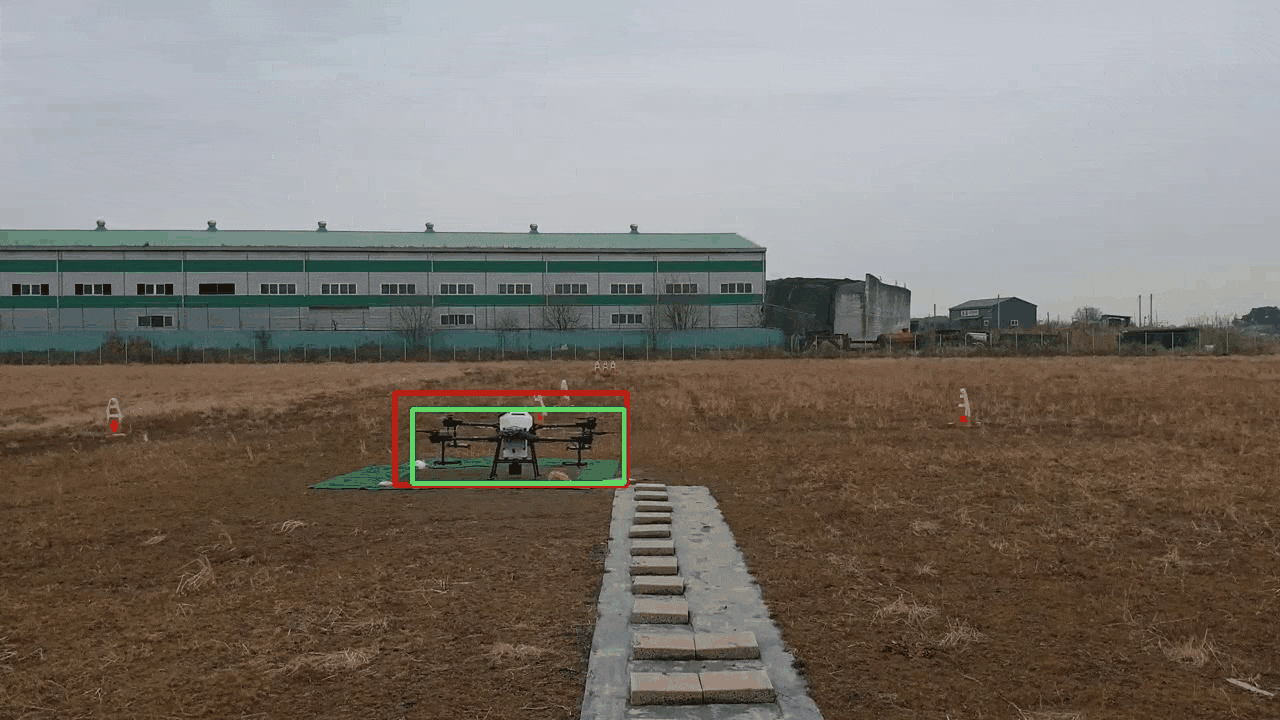
YOLOv5 와 Dual Kalman Filter 기반의 폐색영역에 강건한 객체 추적 프레임워크
김다솔, 허재석*
@article{kim2023yolov5dkf,
title={YOLOv5 와 Dual Kalman Filter 기반의 폐색영역에 강건한 객체 추적 프레임워크},
author={김다솔 and 허재석},
journal={한국정보기술학회논문지},
volume={21},
number={2},
pages={19--32},
year={2023}
}
Although YOLO(You Only Look Once) is a widely used algorithm in real-time object detection, it has a limitation in that its performance significantly deteriorates in occlusion areas where a detection target is obscured by another object or surrounding background. In this study, we propose a robust object tracking framework that utilizes YOLOv5 and a Dual Kalman Filter(KF) consisting of Detection and Inference KFs to address this issue. The proposed framework uses the Detection KF updated with a high weight on the detection results of YOLOv5 when YOLOv5 fails to detect objects. If the object is not detected over successive frames, the proposed framework attempts to track the object using the Inference KF updated with a high weight on the prediction results of KF. Through experiments using data with occluded regions, we confirmed that the proposed framework outperformed existing approaches in terms of detection accuracy while sacrificing less computation speed.
한국정보기술학회논문지, 2023
|
|
A study on market segmentation based on e-commerce user reviews using clustering algorithm
김민경, 허재석*, 사애진, 전아름, 이한별
@article{kim2022jsbs,
title={A study on market segmentation based on e-commerce user reviews using clustering algorithm},
author={Kim, Mingyeong and Huh, Jaeseok and Sa, Aejin and Jun, Ahreum and Lee, Hanbyeol},
journal={Journal of Society for e-Business Studies},
volume={27},
number={2},
pages={103--122},
year={2022}
}
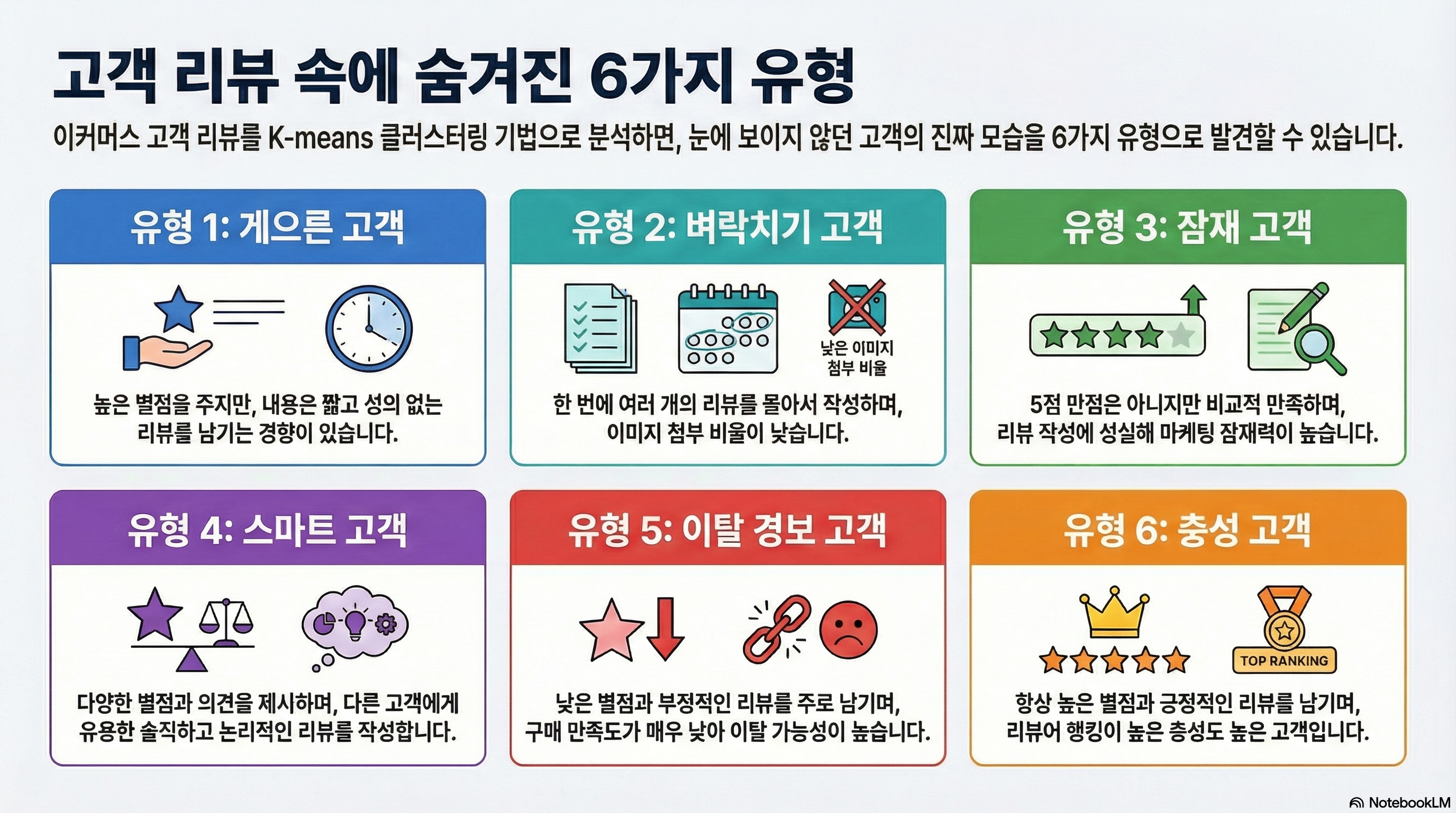
Recently, as COVID-19 has made the e-commerce market expand widely, customers who have different consumption patterns appear in the market. Because companies can obtain opinions and information of customers from reviews, they increasingly face the requirements of managing customer reviews on online platforms. In this study, we analyze customers and carry out market segmentation for classifying and defining types of customers in e-commerce. Specifically, K-means clustering was conducted on customer review data collected from Wemakeprice online shopping platform, which leads to the result that six clusters were derived. Finally, we define the characteristics of each cluster and propose a customer management plan. This study can be used as a reference to identify types of customers, reduce the cost of customer management, and increase profit for online platforms.
한국전자거래학회지, 2022
|
|
인공신경망 가중치의 효과적인 최적화를 위한 하이브리드 메타휴리스틱 알고리즘
고광종, 허재석*
@article{ko2022jkie,
title={인공신경망 가중치의 효과적인 최적화를 위한 하이브리드 메타휴리스틱 알고리즘},
author={Ko, Gwang-Jong and Huh, Jaeseok},
journal={Journal of the Korean Institute of Industrial Engineers},
volume={48},
number={2},
pages={227--234},
year={2022}
}
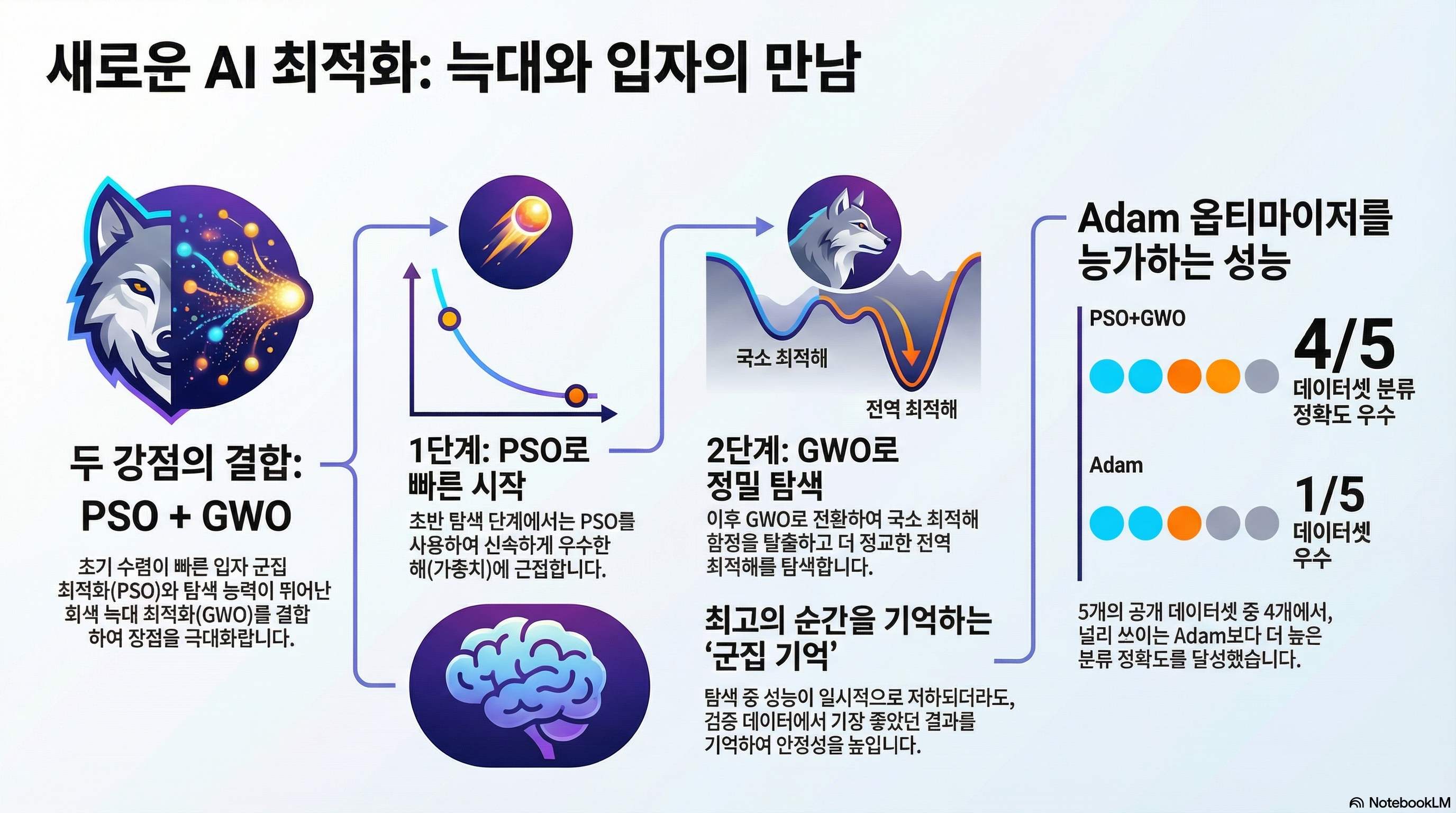
Due to the existence of numerous local minima, gradient descent methods face difficulties in searching for the optimal weights of artificial neural networks (ANNs). To address this, recent studies have explored the use of metaheuristics for ANN weight optimization, with swarm intelligence algorithms showing particular promise. In this study, we propose a hybrid metaheuristic algorithm that combines particle swarm optimization (PSO) and grey wolf optimizer (GWO), both swarm intelligence approaches, to effectively optimize ANN weights. During the search process, the proposed method leverages a swarm memory mechanism inspired by survival behaviors in nature to mitigate convergence instability on validation datasets. Numerical experiments demonstrate that the proposed algorithm outperforms conventional swarm intelligence algorithms, stochastic gradient descent, and Adam optimizer in terms of classification accuracy.
대한산업공학회지, 2022
|
|
제조라인의 학습기반 디스패처를 위한 디스패치 의사결정 평가 시각화시스템
허재석*, 박종헌
@article{huh2020decision,
title={A Decision Monitoring System for Machine Learning Based Dispatcher of Manufacturing Lines},
author={Huh, Jaeseok and Park, Jonghun},
journal={Journal of Society for e-Business Studies},
volume={25},
number={1},
year={2020}
}
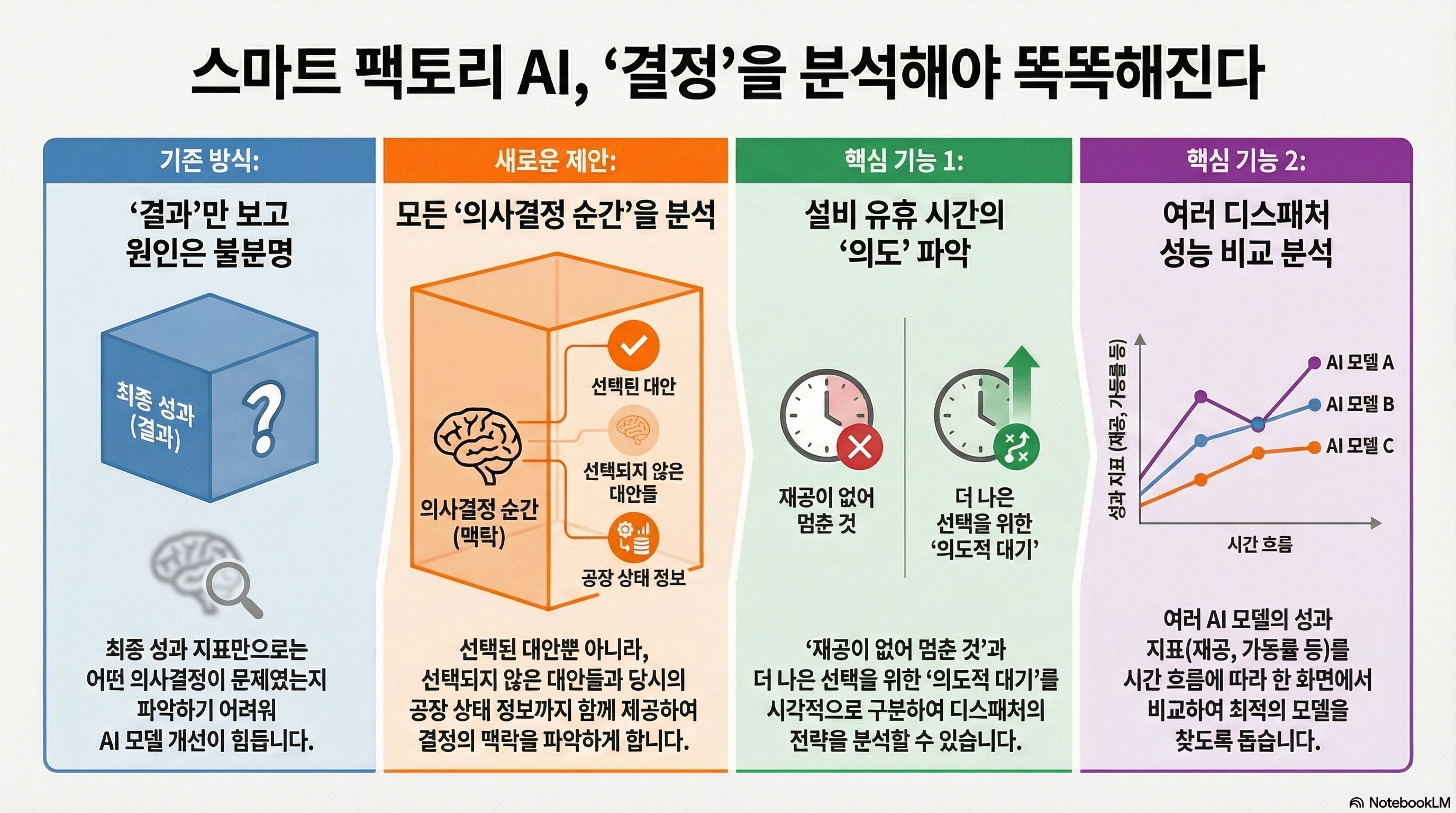
Recently, research using machine learning have shown remarkable results in various domains, leading to the fact that leaning-based dispatchers have intrigued interest in both academia and industry. To improve the performance of the dispatcher, each dispatch decision needs to be evaluated in detail. However, existing studies on visualization techniques for manufacturing lines have mainly focused on illustrating the performance indicators or abnormal patterns. In this paper, we propose a monitoring system that displays a variety of information about the manufacturing line along with alternatives at the time of each dispatching decision being made. Furthermore, the proposed system effectively represents the cause of the idle time of resources and the change of the performance index over time.
전자거래학회지, 2020
|
|
재유입 다중칩 조립라인을 위한 인공신경망 기반의 다중 목적 함수 디스패치 규칙 선택 기법
허재석*, 박종헌
@article{허재석2019재유입,
title={재유입 다중칩 조립라인을 위한 인공신경망 기반의 다중 목적 함수 디스패치 규칙 선택 기법},
author={허재석 and 박종헌},
journal={한국정보기술학회논문지},
volume={17},
number={2},
pages={1--11},
year={2019}
}
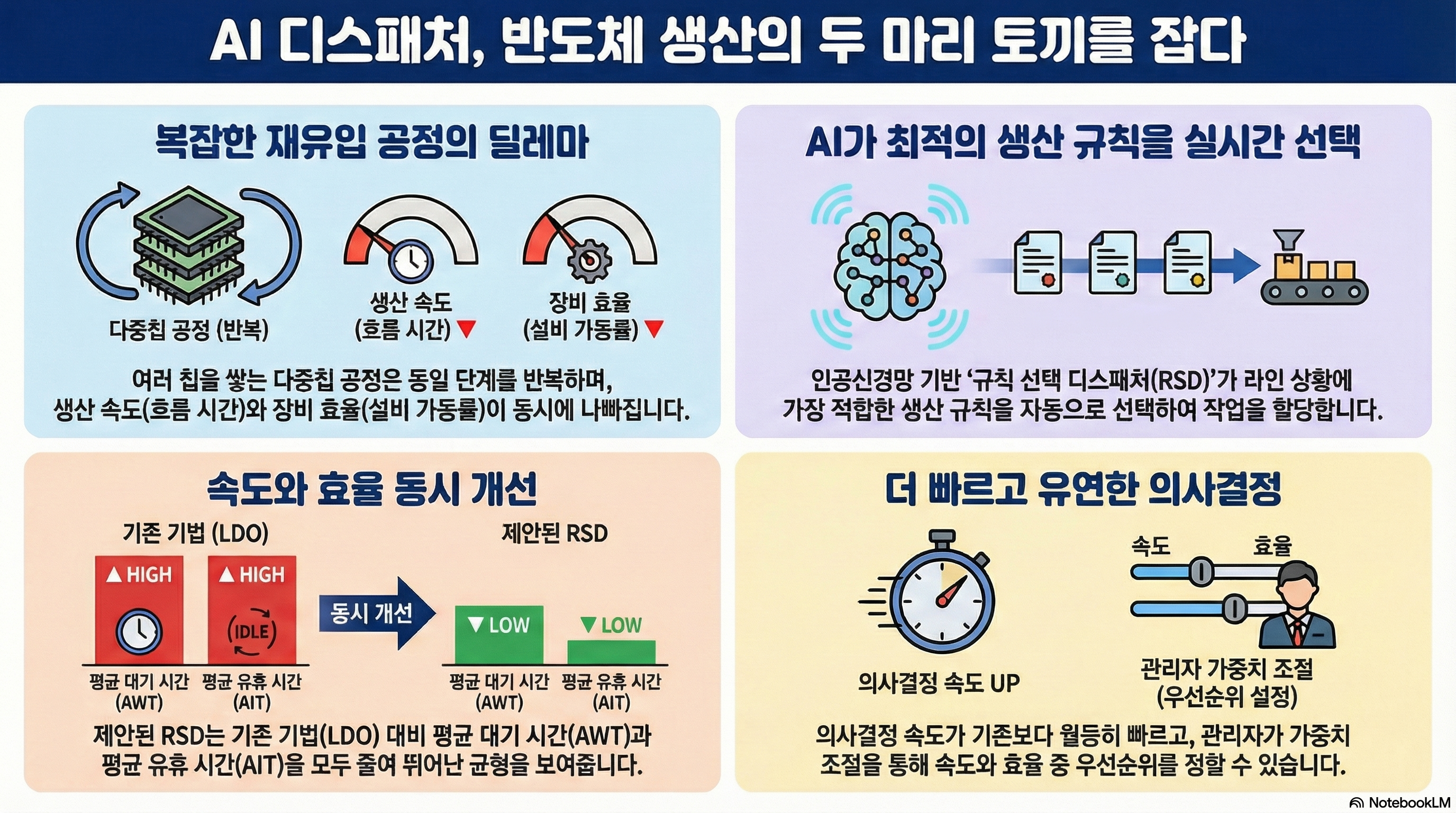
Recently, research using machine learning have shown remarkable results in various domains, leading to the fact that leaning-based dispatchers have intrigued interest in both academia and industry. To improve the performance of the dispatcher, each dispatch decision needs to be evaluated in detail. However, existing studies on visualization techniques for manufacturing lines have mainly focused on illustrating the performance indicators or abnormal patterns. In this paper, we propose a monitoring system that displays a variety of information about the manufacturing line along with alternatives at the time of each dispatching decision being made. Furthermore, the proposed system effectively represents the cause of the idle time of resources and the change of the performance index over time.
한국정보기술학회논문지, 2019
|















